Product Description
Product Description
Roller Chains – ANSI, BS/DN, Anti-Corrosive and Attachment Types
Roller chains are important components and accessories in the whole conveyor belt system. They are used combined with roller sprockets as drive system to ensure the stable and smooth conveying and transmitting. We can supply all kinds of roller chains for you. Just refer to the following introduction, and decide which 1 is suitable for you. As for the detailed specifications, you can get them in 3 ways:
ANSI standard roller chains are the most widely used power transmission chains in the USA. A true powerhouse in precision & quality, the Nitro ANSI chains are built to handle a broad range of applications across many industries. Rigorous quality standards ensures every chain consistently adheres to our requirements for strength and dependability. ANSI chains come in a several options including multiple strands for applications with higher horsepower requirements.
| Chain Number | Pitch | Inner Width | Roller Diameter | Overall Width | Pin Diameter | Plate Height | Plate Thickness |
| # | P | b1 | d1 | L | d2 | h2 | T |
| 25-1* | 1/4 | 1/8 | 0.130 | 0.311 | 0.091 | 0.228 | 0.030 |
| 35-1* | 3/8 | 3/16 | 0.200 | 0.488 | 0.141 | 0.346 | 0.050 |
| 40-1 | 1/2 | 5/16 | 0.312 | 0.653 | 0.156 | 0.469 | 0.060 |
| 41-1 | 1/2 | 1/4 | 0.306 | 0.541 | 0.141 | 0.390 | 0.050 |
| 50-1 | 5/8 | 3/8 | 0.400 | 0.815 | 0.200 | 0.585 | 0.080 |
| 60-1 | 3/4 | 1/2 | 0.469 | 1.571 | 0.234 | 0.709 | 0.094 |
| 80-1 | 1 | 5/8 | 0.625 | 1.287 | 0.312 | 0.949 | 0.125 |
| 100-1 | 1-1/4 | 3/4 | 0.750 | 1.590 | 0.375 | 1.188 | 0.156 |
| 120-1 | 1-1/2 | 1 | 0.875 | 1.980 | 0.437 | 1.425 | 0.187 |
| 140-1 | 1-3/4 | 1 | 1.000 | 2.141 | 0.500 | 1.663 | 0.219 |
| 160-1 | 2 | 1-1/4 | 1.125 | 2.551 | 0.562 | 1.889 | 0.250 |
| 180-1 | 2-1/4 | 1-13/32 | 1.406 | 2.866 | 0.687 | 2.047 | 0.281 |
| 200-1 | 2-1/2 | 1-1/2 | 1.562 | 3.161 | 0.781 | 2.375 | 0.312 |
| 240-1 | 3 | 1-7/8 | 1.875 | 3.760 | 0.937 | 2.791 | 0.375 |
Incorporating links that are twice as long as standard roller chains, the roller chain is intended for long drives, low-to-moderate-speed applications, and uses sprockets with at least 24 teeth. They have been produced with thicker sides plates in order to handle higher working loads than standard chains. With a more robust side plate, heavy roller chains maintain their strength and stability over longer periods of time.
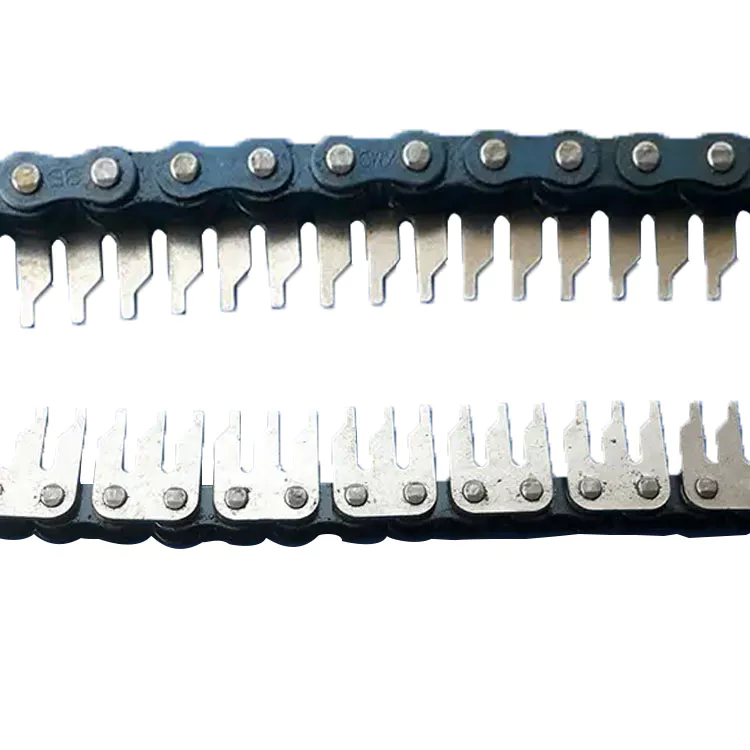
Hollow pin roller chain is essentially the same thing as a standard roller chain just with “hollow-pins”. This not only decreases the chain weight, but it also gives you the ability to place extended pins through the chain for conveying product. Many applications include; bakeries, overhead conveyors, elevators, poultry, agricultural, and a wide range of other applications.
| Size | Pitch (P) | (W) | (R) | (D) | (d) | Hollow Pin Length | (F) | (H) | (T) | Weight |
| 40HP | 0.500″ | 0.313″ | 0.312″ | 0.221″ | 0.157″ | 0.689″ | 0.689″ | 0.472″ | 0.059″ | 0.35 LBS/ FT |
| 50HP | 0.625″ | 0.375″ | 0.400″ | 0.283″ | 0.202″ | 0.854″ | 0.854″ | 0.591″ | 0.079″ | 0.58 LBS/ FT |
| 60HP | 0.750″ | 0.500″ | 0.469″ | 0.333″ | 0.236″ | 1.055″ | 1.055″ | 0.713″ | 0.094″ | 0.81 LBS/ FT |
| 80HP | 1.000″ | 0.625″ | 0.625″ | 0.449″ | 0.318″ | 1.276″ | 1.276″ | 0.950″ | 0.125″ | 1.46 LBS/ FT |
|
| Size | Pitch (P) | (K) | (W) | (R) | (D) | (F) | (T1) | (T2) | (H) | Weight (LBS/ FT) | ||
| 04B-2 | 0.236″ | 0.217″ | 0.110″ | 0.158″ | 0.073″ | 0.524″ | — | — | 0.197″ | 0.154 | ||
| 05B-2 | 0.315″ | 0.222″ | 0.118″ | 0.197″ | 0.091″ | 0.571″ | — | — | 0.280″ | |||
| 06B-2 | 0.375″ | 0.403″ | 0.225″ | 0.250″ | 0.129″ | 0.941″ | 0.039″ | 0.051″ | 0.323″ | 0.496 | ||
| 08B-2 | 0.500″ | 0.548″ | 0.305″ | 0.335″ | 0.175″ | 1.260″ | 0.059″ | 0.059″ | 0.469″ | 0.872 | ||
| 10B-2 | 0.625″ | 0.653″ | 0.380″ | 0.400″ | 0.200″ | 1.457″ | 0.059″ | 0.059″ | 0.579″ | 1.127 | ||
| 12B-2 | 0.750″ | 0.766″ | 0.460″ | 0.475″ | 0.225″ | 1.697″ | 0.071″ | 0.071″ | 0.634″ | 1.529 | ||
| 16B-2 | 1.000″ | 1.255″ | 0.670″ | 0.625″ | 0.326″ | 2.756″ | 0.126″ | 0.157″ | 0.819″ | 3.433 | ||
| 20B-2 | 1.250″ | 1.435″ | 0.770″ | 0.750″ | 0.401″ | 3.169″ | 0.138″ | 0.177″ | 1.571″ | 5.076 | ||
| 24B-2 | 1.500″ | 1.904″ | 1.000″ | 1.000″ | 0.576″ | 4.217″ | 0.197″ | 0.236″ | 1.224″ | 9.321 | ||
| 28B-2 | 1.750″ | 2.345″ | 1.220″ | 1.100″ | 0.626″ | 5.083″ | — | — | 1.457″ | 11.09 | ||
| 32B-2 | 2.000″ | 2.305″ | 1.220″ | 1.150″ | 0.701″ | 5.102″ | — | — | 1.662″ | 14.571 | ||
| 40B-2 | 2.500″ | 2.846″ | 1.500″ | 1.550″ | 0.901″ | 6.358″ | — | — | 2.083″ | 21.378 | ||
| 48B-2 | 3.000″ | 3.599″ | 1.800″ | 1.900″ | 1.151″ | 7.803″ | — | — | 2.512″ | 33.4 | ||
| 56B-2 | 3.500″ | 4.197″ | 2.100″ | 2.125″ | 1.351″ | 9.039″ | — | — | 3.063″ | 46.765 |
Certifications
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Metal Conveyor Belt |
|---|---|
| Material: | Metal |
| Inside Material: | Metal |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do you calculate the chain pull force in a conveyor chain system?
The chain pull force, also known as the chain tension, is an important parameter to determine in a conveyor chain system. It represents the force required to move the conveyed load along the conveyor. The calculation of chain pull force involves several factors:
1. Weight of the Load: Determine the weight of the load being conveyed. This includes the weight of the product, packaging materials, and any additional equipment or components carried by the conveyor.
2. Friction Coefficients: Identify the friction coefficients between the load and the conveyor components. This includes the friction between the product and the conveyor chain, as well as the friction between the product and the conveyor bed or guides. These coefficients are typically provided by the manufacturer or can be obtained through testing.
3. Incline or Decline Angle: Consider the angle at which the conveyor operates. If the conveyor has an incline or decline, the angle will affect the force required to move the load.
4. Acceleration and Deceleration: Account for any acceleration or deceleration requirements in the conveyor system. If the conveyor needs to start or stop abruptly or if there are changes in speed, these factors will impact the chain pull force.
Once these factors are determined, the chain pull force can be calculated using the following formula:
Chain Pull Force = (Weight of Load + Friction Force) × (1 + Incline or Decline Factor) × (1 + Acceleration or Deceleration Factor)
It’s important to note that the accuracy of the calculation depends on the accuracy of the input values. Therefore, it’s recommended to consult the conveyor manufacturer or an engineering professional to ensure precise calculations and proper sizing of the conveyor chain.
Can a conveyor chain be used in food processing applications?
Yes, a conveyor chain can be used in food processing applications. Conveyor chains play a crucial role in the efficient and hygienic handling of food products throughout the production process. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Food-Grade Materials: Conveyor chains used in food processing applications are typically made from food-grade materials such as stainless steel or plastic. These materials are corrosion-resistant, easy to clean, and comply with food safety regulations.
2. Hygiene Considerations: Food processing environments require high standards of hygiene. Conveyor chains designed for food applications incorporate features such as smooth surfaces, open link designs, and easy disassembly for thorough cleaning. They may also have specialized coatings or treatments to prevent bacterial growth.
3. Sanitary Design: Conveyor chains for food processing applications are designed with minimal crevices or joints to prevent food particles from getting trapped. They may have self-draining capabilities to remove excess fluids or debris.
4. Product Integrity: Conveyor chains in food processing applications ensure gentle handling of delicate food products to avoid damage or contamination. They can be equipped with accessories like cleats, side guards, or modular belt systems to securely hold and transport items of various shapes and sizes.
5. High Temperature and Washdown Capabilities: Some food processing applications require conveyor chains to withstand high temperatures during cooking, baking, or sterilization processes. Specialized chains with heat-resistant materials or coatings are available. Additionally, conveyor chains used in food processing should be capable of withstanding frequent washdowns and cleaning with water or cleaning agents.
6. Compliance with Standards: Conveyor chains used in food processing applications must comply with industry-specific standards such as FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regulations, HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) guidelines, and other food safety certifications.
When selecting a conveyor chain for food processing applications, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the production line, including the type of food being handled, the operating conditions, and the necessary sanitary standards. Proper maintenance and regular cleaning protocols should also be implemented to ensure food safety and product integrity.

What are the main components of a conveyor chain?
The main components of a conveyor chain include:
- Chain Links: Chain links are the individual components that make up the conveyor chain. They are typically made of metal and are connected to form a continuous loop. The design and configuration of the chain links can vary depending on the specific application and load requirements.
- Pins: Pins are the cylindrical components that hold the chain links together. They are inserted through the end of each chain link to create a solid connection. Pins are usually made of hardened steel to withstand the forces and friction within the conveyor system.
- Sprockets: Sprockets are toothed wheels that engage with the chain links and provide the driving force to move the conveyor chain. They are typically made of durable materials such as steel or plastic and are designed to match the pitch and profile of the conveyor chain. Sprockets come in various sizes and configurations depending on the desired speed and load capacity of the conveyor system.
- Guide Rails: Guide rails are stationary components installed along the conveyor path to guide and support the movement of the conveyor chain. They help maintain proper alignment and prevent the chain from derailing or deviating from its intended path.
- Tensioners: Tensioners are devices used to maintain the proper tension in the conveyor chain. They ensure that the chain remains taut and engaged with the sprockets, preventing slack or excessive sagging. Tensioners can be adjusted to accommodate variations in chain length and to compensate for wear over time.
- Attachments and Accessories: Depending on the specific application, conveyor chains may include various attachments and accessories. These can include cleats, flights, buckets, or other devices that aid in the movement and handling of specific types of materials. These attachments are typically secured to the chain links at specific intervals or locations.
The combination of these components creates a robust and reliable conveyor chain system capable of efficiently transporting materials in a wide range of industrial applications.


editor by CX 2023-12-29